Getting all flags
Read time: 13 minutes
Last edited: Nov 19, 2024
Overview
This topic explains how the all flags feature works in the LaunchDarkly SDKs that support it. The all flags feature is available for client-side, server-side, and edge SDKs.
A context is a generalized way of referring to the people, services, machines, or other resources that encounter feature flags in your product. Contexts replace another data object in LaunchDarkly: "users."
Creating contexts and evaluating flags based on them is supported in the latest major versions of most of our SDKs. For these SDKs, the code samples on this page include the two most recent versions.
About the all flags feature
The all flags feature returns an object containing the variation values of all the feature flags targeted to a specific context object or user object.
Server-side SDKs also return metadata for use on the front end, including information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. You can use this metadata to provide bootstrap flag settings for LaunchDarkly's JavaScript-based SDKs. To learn more, read the JavaScript SDK reference.
You can find the expected flag values for a specific context on its details page:
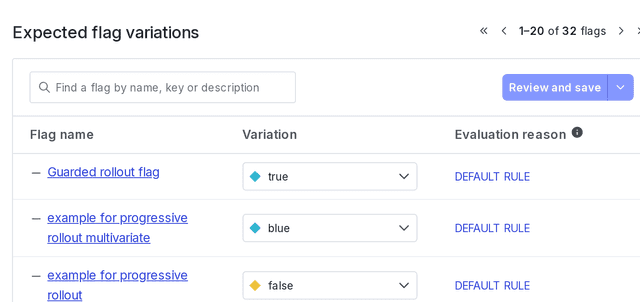
The all flags method does not send analytics events to LaunchDarkly by default for most SDKs. The exceptions to this are Electron, JavaScript, Node.js (client-side), and Vue, which do send analytics events by default. For these SDKs, you can disable sending analytics events when calling the all flags method if needed. To learn more about what analytics events do in LaunchDarkly, read Analytics events.
For client-side SDKs, the all flags feature may return a null value in cases where a flag's fallback value would be served to the end user.
For server-side SDKs, you can use the all flags feature to pass feature flags to your front end. In particular, you can use it to provide bootstrap flag settings for the JavaScript SDK. To learn more about bootstrapping from a client-side SDK, read Bootstrapping.
Details about each SDK's configuration are available in the SDK-specific sections below:
Client-side SDKs
Before you implement this feature, read About the all flags feature.
This feature is available in the following client-side SDKs:
- .NET (client-side)
- Android
- C++ (client-side)
- Electron
- Flutter
- iOS
- JavaScript
- Node.js (client-side)
- React Native
- React Web
- Roku
.NET (client-side)
Expand .NET (client-side) code sample
The AllFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
Android
Expand Android code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
C++ (client-side)
Expand C++ (client-side) code sample
The AllFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object:
To learn more, read AllFlags in the Client documentation.
Electron
Expand Electron code sample
The allFlags() method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a user object. The map contains null values for any flags that would return the fallback value. The fallback value is the second argument that you normally pass to variation.
Unlike most of our SDKs, our Electron SDK's allFlags() method sends analytics events to LaunchDarkly. If you do not want allFlags() to generate any analytics events, you can turn this off by setting the configuration option sendEventsOnlyForVariation to true.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
Flutter
Expand Flutter code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object:
To learn more, read allFlags.
iOS
Expand iOS code sample
The all flags method produces a dictionary of feature flag keys to their values for a context object. If the LDClient is not started, it returns nil.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read the API documentation for Swift or Objective-C.
JavaScript
Expand JavaScript code sample
The allFlags() method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object.
The map contains null values for any flags that would return the fallback value. The fallback value is the second argument that you normally pass to variation.
Unlike most of our SDKs, our JavaScript SDK's allFlags method sends analytics events to LaunchDarkly. If you do not want allFlags to generate any analytics events, you can turn this off by setting the configuration option sendEventsOnlyForVariation to true.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Node.js (client-side)
Expand Node.js (client-side) code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object.
The map contains null values for any flags that would return the fallback value. The fallback value is the second argument that you normally pass to variation.
Unlike most of our SDKs, our Node.js (client-side) SDK's allFlags method sends analytics events to LaunchDarkly. If you do not want allFlags to generate any analytics events, you can turn this off by setting the sendEventsOnlyForVariation option to true.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
React Web
Expand React Web code sample
The allFlags() method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object. The React Web SDK relies on the JavaScript SDK for its allFlags functionality.
Here is an example:
By default, the React Web SDK does not send analytics events for allFlags. It only sends analytics events for variation or useFlags calls. Analytics events include feature events, debug events, and evaluation events. This behavior matches the behavior of most of our SDKs, but differs from the behavior of the JavaScript SDK. To learn more, read About the all flags feature, above.
If you do need to generate analytics events for the allFlags method, you can set the sendEventsOnlyForVariation configuration option to false. We do not recommend this, because then you will receive events for all flags. You will have no way to differentiate events for flags that are in use from events for flags that are not in use.
React Native
Expand React Native code sample
The allFlags method returns a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context, or an empty object if flags cannot be evaluated.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read allFlags.
Roku
Expand Roku code sample
The all flags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a context object:
Server-side SDKs
Before you implement this feature, read About the all flags feature.
This feature is available in the following server-side SDKs:
- .NET (server-side)
- Apex
- C++ (server-side)
- Erlang
- Go
- Haskell
- Java
- Lua
- Node.js (server-side)
- PHP
- Python
- Ruby
- Rust
.NET (server-side)
Expand .NET (server-side) code sample
The AllFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Apex
Expand Apex code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values for a specific user object:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
C++ (server-side)
Expand C++ (server-side) code sample
The AllFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context. Here's how to call it and output the result:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Erlang
Expand Erlang code sample
The all_flags_state method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Go
Expand Go code sample
The AllFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
This example specifies the extra ClientSideOnly option so that only the feature flags designated for client-side use are included in the result.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Haskell
Expand Haskell code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Java
Expand Java code sample
The allFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object:
To learn more, read allFlagsState.
Lua
Expand Lua code sample
The allFlags method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context.
Here's how to call it and output the result:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read [allFlags]](https://launchdarkly.github.io/lua-server-sdk/modules/launchdarkly-server-sdk.html#allFlags).
Node.js (server-side)
Expand Node.js (server-side) code sample
The allFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
PHP
Expand PHP code sample
The allFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Python
Expand Python code sample
The all_flags_state method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Ruby
Expand Ruby code sample
The all_flags_state method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Rust
Expand Rust code sample
The all_flags_detail method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object:
The metadata includes information on flag keys, variations, and prerequisites. To learn more, read the API documentation.
Edge SDKs
Before you implement this feature, read About the all flags feature.
This feature is available for the following edge SDKs:
Akamai
Expand Akamai code sample
The allFlagsState method produces an object that encapsulates the state of all feature flags for a given context. This method does not send analytics events back to LaunchDarkly.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
Cloudflare
Expand Cloudflare code sample
The allFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read the API documentation.
allFlagsState does not generate eventsThe Cloudflare SDK supports sending events. However, the allFlagsState method does not generate events in edge SDKs. Use the variation method instead. To learn more, read Evaluating flags.
Vercel
Expand Vercel code sample
The allFlagsState method produces a map of feature flag keys to their values and other metadata for a specific context object.
To use the all flags feature:
To learn more, read allFlagsState.
allFlagsState does not generate eventsThe Vercel SDK supports sending events. However, the allFlagsState method does not generate events in edge SDKs. Use the variation method instead. To learn more, read Evaluating flags.