Targeting with migration flags
Read time: 3 minutes
Last edited: Nov 12, 2024
Overview
This topic explains how to target contexts with migration flags.
Targeting variations and stages
The different stages of a migration flag are expressed by the flag's variations. Migration flags have built-in variations that you cannot edit, because they are linked to the migration's stages. To progress through stages in a migration, adjust the percentage rollout to serve a different variation to a larger group, until 100% of contexts receive the same variation. We recommend progressing through the stages in the order they're presented.
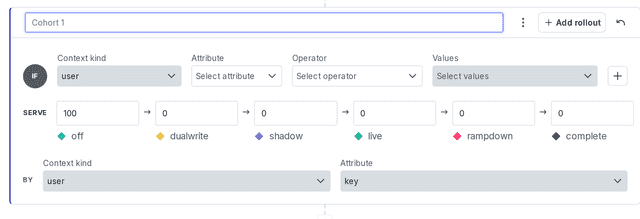
Targeting cohorts
Migration flag cohorts are analogous to the targeting rules for other types of feature flags. The default cohort is analogous to the default rule.
You can target cohorts in mostly the same ways you target rules, but cohorts always serve a percentage rollout. This helps visualize the progress of a migration. To learn more about rollouts, read Percentage rollouts.
You must specify a default cohort that this flag targets when the contexts specified in it are not a part of any other cohort. We recommend allocating 100% of this cohort in the "off" stage.
Here's how to create a cohort:
- Navigate to a migration flag's Targeting tab.
- Click + Add cohort and choose "Target segments" or "Build a custom rule."
- Configure the cohort's targeting information. To learn more, read Target with flags.
- In the "Serve" section, allocate the cohort into flag variations by percentages between 0 and one hundred. The total number in all stages must equal one hundred.
Targeting contexts
You cannot target individual contexts with a migration flag. If you need to target an individual context, create a cohort that contains only that context.
Migration flags' off variations
The off variation for a migration flag is always off. This ensures that migrations always begin in the correct stage.
Understanding restrictions for migration flags with six stages
Migrations with six stages require you to specify a context kind to represent how the migrated data is partitioned. This context kind only targets contexts for the migration flag.
Migration flags with six stages have the following restrictions:
- When you adjust a rollout, it will only affect keys for the context kind you designated for the six-stage migration
- You can only create cohort clauses that reference that context kind
- Cohorts cannot use the
segmentMatchoperator because segments can reference other context kinds - You cannot add prerequisites, because they can reference other context kinds
To learn more about when to use two, four, or six-stage migrations, read Performing multi-stage migrations with migration flags.
Understanding potential migration issues
Some targeting actions may create issues that could impact your data integrity. If a scenario like this occurs, a warning appears when you try to save.
Examples of actions that may cause safety issues are:
- Adding a cohort that causes reads from the new system when a later cohort is not backfilled or in the
offstage - Removing a cohort that is not backfilled or in the
offstage when a later cohort causes reads - Reordering a cohort that is not backfilled or in the
offstage when a later cohort (from its old position) causes reads from the new system
You can also use the REST API: Get migration safety issues