Metrics
Read time: 7 minutes
Last edited: Jul 02, 2024
Metrics is available to customers on a Pro or Enterprise plan. To learn more, read about our pricing. To add Experimentation to your plan, contact Sales.
Overview
This topic explains how to create and use metrics within LaunchDarkly.
Metrics measure audience behaviors affected by flags. You can use metrics to track all kinds of things, from how often customers access a URL to how long that URL takes to load a page. Create metrics that align with your business goals and connect them to your team's flags to track the impact of different flag variations over time.
To view your list of metrics, navigate to the Metrics list:
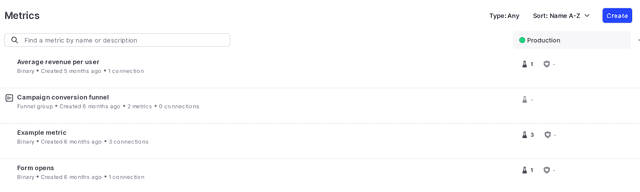
To learn how to create, edit, and delete metrics, read Creating metrics.
You can also use the REST API: Metrics
The metric details page
From the Metrics list, click on a metric or metric group to view its details.
The metric details page displays the metric or metric group's:
- Name
- Description
- Maintainer
- Event kind:
customconversion or binary,click, orpage view - Event key: the value you insert into your code to track events
- Tags
- Metric connections
LaunchDarkly automatically generates a metric key when you create a metric. You can use the metric key to identify the metric in API calls. To learn more, read Creating metrics.
Custom conversion/binary and custom numeric metrics also require an event key. You can set the event key to anything you want. Adding this event key to your codebase lets your SDK track actions customers take in your app as events. To learn more, read Sending custom events.
Measurement definition
The "Measurement definition" section of the right sidenav displays the following information:
- Randomization unit
- Aggregation method: by average or by sum
- Analysis method: by mean or by percentile
- For numeric metrics only: whether it's better for this metric to increase or decrease
- For numeric metrics only: unit of measure
- Units without events:
Exclude units without events from the analysis, orSet the value for units with no events to zero

Metric connections
The "Metric connections" section of the right sidenav displays a summary of experiments, metric groups, and legacy experiments the metric is included in, either currently or previously.
To view a detailed list of metric connections, click the expand icon in the "Metric connections" section of the right sidenav:

The expanded metric connections view includes:
- Experiment: the name of the experiment.
- Experiment status: whether the experiment is not started, running or stopped.
- Environment: the environment the experiment is in.
- Metric status: when LaunchDarkly last received events from this metric.
- Effect size from control: the difference in performance for the variation being tested against the control variation.
Metric event activity
The metric event activity tab provides visibility into the events LaunchDarkly is receiving for custom numeric and custom conversion metrics. The activity tab does not display events for click or page view metrics.
The activity tab includes information for the most recently received event, and for the last 100 events received within two hours of that event.
For each event, the activity tab displays:
- Timestamp: when the metric received the event.
- Context key: the key of the context that generated the event.
- Value: for custom numeric metrics, the numeric value of the event.
To view more information about a specific event, click on the event row. An "Event details" dialog appears:

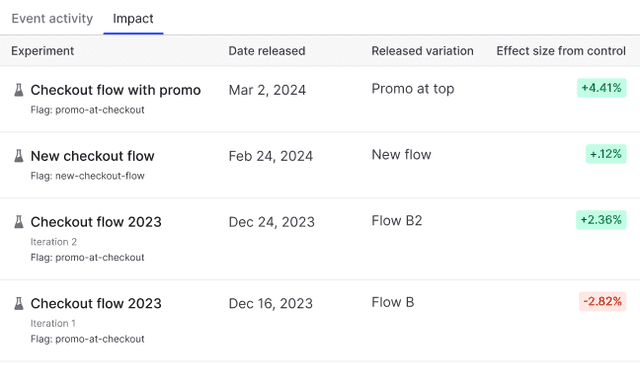
Metric impact
The metric impact tab displays a list of complete experiment iterations that used the metric. Any experiment iterations that are currently running do not display on this list. This helps you understand how different flag variations have impacted the metric as part of your Experimentation program.
This list includes:
- The name of the experiment or flag the metric was attached to.
- The date the experiment iteration or guarded rollout ended.
- The variation rolled out to all contexts at the end of the experiment iteration or guarded rollout.
- The effect size from control, which is the difference in performance for the variation being tested against the control variation.
You can also use the REST API: Get metric
Metric events
An "event" happens when an end user takes an action in your app, such as clicking on a button, or when a system takes an action, such as loading a page. Your SDKs send these events to LaunchDarkly, where LaunchDarkly metrics can aggregate and analyze them. LaunchDarkly can then quantify the overall performance and health of your product and provide suggestions on how to respond.
There are three types of metric events:
customevents are produced by custom conversion/binary metrics and custom numeric metrics- Conversion/binary metrics register events when an end user takes an action based on a feature flag they encounter
- Numeric metrics measure numeric values against a baseline you set
clickevents are produced by custom click metricspage viewevents are produced by custom page view metrics
You can send custom events using the track feature in your SDK. To learn more about event kinds, read Event kinds. To learn more about Experimentation events, read Experimentation events.
Try it in your SDK: Sending custom events
The following table explains the kinds of events you can track with a metric and their SDK compatibility:
| Event kind | Metric | Description | SDK compatibility |
|---|---|---|---|
| Custom | Conversion/binary | Tracks events for any arbitrary event. | All |
| Custom | Numeric | Tracks increases or decreases in numeric value against a baseline you set. | All |
| Click | Conversion | Tracks the clicks on a user interface (UI) element. | Electron JavaScript Node.js (client-side) React Web Vue |
| Page view | Conversion | Tracks how many times a page is viewed. | Electron JavaScript Node.js (client-side) React Web Vue |
To learn more about different metric types and when to use them, read Choose a metric type.
For examples of common metrics and how to configure them, read Example metrics.
Event keys
When you create a custom conversion/binary or custom numeric metric, you must set an event key for the metric. You will use this event key in your codebase to track actions taken by your users or other contexts. You can set the event key to anything you want, and it may already exist in your codebase.
The event key in your metric and the event key in your code must match exactly. This lets your SDK track actions customers take in your app as events.
To learn more, read Sending custom events.
Metric versions
When you create a new metric, the metric has a version of 1. Each time you edit and save the metric, LaunchDarkly increments the metric version. This ensures that experiments, measured releases, and other features continue to display the correct analysis for the metric as it was configured at the time of its use. If you make edits to a metric currently in use, any LaunchDarkly feature using it will continue to use the old version of the metric.
For example, if you create an experiment using version 1 of a metric, then edit the metric while the experiment is running, the experiment will continue to use version 1 of the metric until you stop the experiment iteration. This ensures the experiment analysis is valid. Any new iterations of the experiment you begin later will then use version 2 of the metric.
Metric groups
A metric group is a reusable, ordered list of metrics you can use to standardize metrics across multiple experiments and flags. To learn more, read Metric groups.